Navigating Media Literacy in Politics
Media literacy is the ability to access, analyze, and evaluate various forms of communication. It encompasses understanding how media messages are constructed, the motives behind these messages, and the ways in which media can influence and shape public opinion and behavior. Media literacy is essential in today’s digital world, where information is abundant and can easily spread. By understanding media literacy, you can empower yourself to understand the impact of the media you consume and make informed decisions based on what you read, hear, or see.
Understanding Media Bias
Understanding media bias is crucial in politics. Bias refers to the favoring of a particular perspective or point of view, which can influence how information is presented. It is important to recognize that all media outlets have some level of bias, whether it is conscious or unconscious.
One way to identify media bias is to be aware of the language used in news articles or reports. Pay attention to the tone, choice of words, and the framing of the information. Biased media outlets may use emotionally charged language, sensationalize stories, or present information in a way that supports their own agenda.
Another way to understand media bias is to compare coverage of the same event or topic across different news sources. By consuming news from a variety of sources, you can get a more well-rounded view and identify any biases that may exist.
Ad Fontes Media is a well known source for evaluating media bias, and has an interactive chart that shows exactly where the source you get your information from sits on the scale.
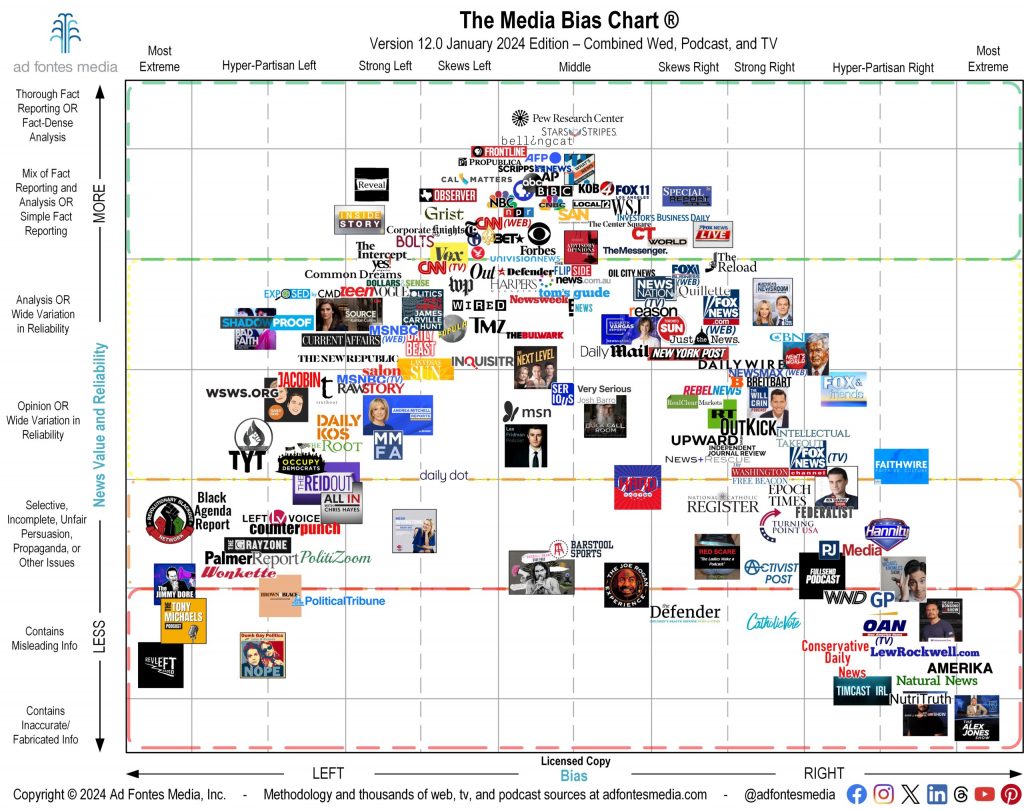
It is important to approach media consumption with a critical mindset and question the information presented. By understanding media bias, you can navigate the political landscape more effectively and make informed decisions.
Evaluating Sources of Information
In order to navigate media literacy in politics, it is essential to evaluate the sources of information you rely on. Not all sources are created equal, and some may have their own biases or agendas.
When evaluating sources, consider the reputation and credibility of the outlet. Look for established news organizations that adhere to journalistic standards and have a history of accurate reporting.
Additionally, consider the expertise and qualifications of the authors or journalists. Are they experts in the field they are reporting on? Do they have a track record of reliable reporting?
It is also important to consider the transparency of the source. Does the outlet provide information about their funding or potential conflicts of interest? Transparency is key to understanding any potential biases that may exist. By evaluating the sources of information, you can ensure that you are consuming reliable and trustworthy news.
Fact-Checking Techniques
Fact-checking is a crucial skill when it comes to media literacy in politics. With the abundance of information available, it is important to verify the accuracy of the claims being made.
One technique for fact-checking is to cross-reference the information with multiple sources. By comparing information from different outlets, you can identify any inconsistencies or discrepancies.
Another technique is to look for primary sources of information. Instead of relying solely on news articles or opinion pieces, seek out original documents, reports, or official statements to verify the facts.
Fact-checking organizations can also be a valuable resource. These organizations specialize in verifying the accuracy of claims made by politicians or in the media. By consulting reputable fact-checkers, you can ensure that the information you are consuming is based on facts.
By employing fact-checking techniques, you can separate fact from fiction and make informed decisions based on accurate information.
A list of fact-checking websites available for use include:
- Politifact
- FactCheck.org
- Washingtion Post Fact Checker
- Snopes
- Fact Check from Duke Reporters’ Lab
- SciCheck
- FlackCheck
- Media Bias/Fact Check
- NPR Fact Check
For more information about these fact-checking sources, visit the College of Staten Island’s Library Research Guide
Navigating Misinformation
Misinformation is false or inaccurate information that is spread unintentionally. It can be challenging to navigate in the realm of media literacy in politics, but there are strategies to help identify and address misinformation.
One strategy is to be mindful of the source of the information. If a piece of information seems too good to be true or comes from an unfamiliar or unreliable source, it is important to verify its accuracy before believing or sharing it.
Another strategy is to critically analyze the content itself. Look for logical inconsistencies, exaggerated claims, or lack of evidence to support the information being presented. Misinformation often relies on emotional appeals rather than factual evidence. Additionally, fact-checking can be a powerful tool in combating misinformation. By verifying the accuracy of claims and sharing reliable information, you can help prevent the spread of false or misleading information.
Navigating misinformation requires a critical and discerning mindset. By being vigilant and questioning the information you encounter, you can avoid being misled by false or inaccurate information.
Combatting Disinformation
Disinformation is intentionally false or misleading information that is spread with the intention to deceive or manipulate. In the realm of media literacy in politics, it is important to be aware of disinformation and take steps to combat it.
One way to combat disinformation is to verify the source of the information. Check if the source is reputable and reliable. Disinformation often comes from anonymous or unreliable sources. Another strategy is to fact-check the information before believing or sharing it. Look for evidence and supporting sources to validate the claims being made. Disinformation often lacks credible evidence. It is also important to be cautious of information that plays on emotions or seeks to divide. Disinformation often uses emotional appeals or promotes divisive narratives to manipulate public opinion.
By being aware of disinformation and taking steps to combat it, you can help promote a more informed and reliable media landscape.
Confirmation Bias
Confirmation bias is the subconscious tendency to seek and interpret information and evidence that affirms our existing beliefs or ideas. It can be most entrenched around beliefs and ideas that we are strongly attached to or that provoke a strong emotional response. It can affect decision-making and critical thinking, making it harder for individuals to objectively evaluate information and consider alternative viewpoints.
Why This Matters
By analyzing the motives behind political messages, individuals can discern the difference between fact and opinion, and identify misinformation or propaganda. Evaluating the credibility of sources and cross-referencing information with multiple outlets ensures a more balanced and accurate understanding of political events. Creating and sharing well-researched content also contributes to a more informed public discourse, especially in today’s world where it seems like every other post on Facebook or Tiktok seems sketchy. Ultimately, media literacy enables individuals to navigate the complex political landscape, make informed decisions, and participate actively in democratic processes

